Rotational Kinetic Energy Calculator
Calculate rotational kinetic energy easily with our online calculator. Get fast, accurate results for any rotating object.
Do you ever wonder about the energy stored in rotating objects? It might sound complex, but calculating rotational kinetic energy doesn’t have to be hard. Whether you're tinkering with machines or diving into physics, you’ll find our Rotational Kinetic Energy Calculator a breeze to use.
This tool is a lifesaver for students, engineers, and anyone else needing to calculate energy in rotating objects. With just a few inputs, you'll get the answers you need.
What is Rotational Kinetic Energy?
Simply put, rotational kinetic energy is the energy an object has because it's spinning. Think about a wheel, a planet, or even a toy top. When they spin, they have energy. The faster they spin, the more energy they store.
Here's the formula to calculate it:
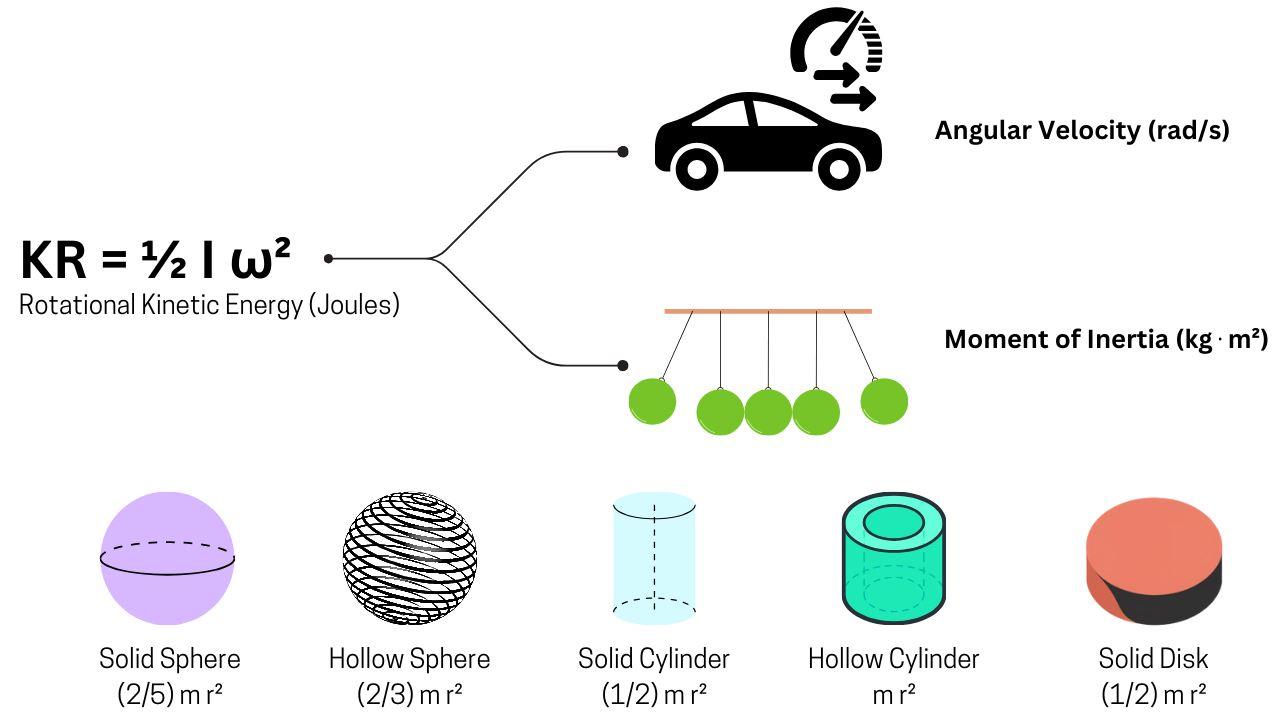
KR = ½ I ω²
Where:
- KR = Rotational Kinetic Energy (Joules)
- I = Moment of Inertia (kg⋅m²)
- ω = Angular Velocity (rad/s)
As you can see, it depends on both the object’s mass distribution (moment of inertia) and how fast it’s spinning (angular velocity). Cool, right?
How to Calculate Rotational Kinetic Energy?
Calculating this is easier than you might think. Here's a step-by-step guide:
Find the Moment of Inertia (I):
The moment of inertia depends on the object’s shape. For example, a solid sphere uses this formula:
I = (2/5) m r²
(Don’t worry, we’ll help you with the math in the calculator.)
Get the Angular Velocity (ω):
Angular velocity is how fast something spins. You can measure it in radians per second (rad/s), or convert from RPM or degrees per second.
Use the Formula:
Once you have these numbers, plug them into this formula:
KR = ½ I ω²
That’s it! Now you know how to calculate rotational kinetic energy.
Common Shapes and Their Inertia
| Object Shape | Moment of Inertia Formula |
|---|---|
| Solid Sphere | (2/5) m r² |
| Hollow Sphere | (2/3) m r² |
| Solid Cylinder | (1/2) m r² |
| Hollow Cylinder | m r² |
| Solid Disk | (1/2) m r² |
How to Use the Rotational Kinetic Energy Calculator?
Our Rotational Kinetic Energy Calculator makes this so much easier! Here’s how it works:
- Enter the Moment of Inertia (I):
Pick the right units (kg⋅m², g⋅cm², lb⋅ft²). - Add the Angular Velocity (ω):
Choose the unit (rad/s, RPM, degrees/s). - Pick the Energy Unit:
Decide whether you want the energy in Joules, Kilojoules, or Foot-pounds. - Hit Calculate!
That’s it! You’ll get your answer instantly.
The calculator saves you from a ton of math and unit conversions, making it a must-have for anyone dealing with rotational motion.
Rotational Kinetic Energy vs. Linear Kinetic Energy
| Type | Formula | Depends On |
|---|---|---|
| Rotational Kinetic Energy | KR = ½ I ω² | Moment of Inertia, Angular Velocity |
| Linear Kinetic Energy | KE = ½ m v² | Mass, Linear Velocity |
Here’s a quick comparison. Rotational kinetic energy is about an object’s spin, while linear kinetic energy is about how fast an object moves in a straight line.
Final Verdict
Our Rotational Kinetic Energy Calculator is a super handy tool for quickly calculating energy in rotating objects. Whether you’re studying physics, working with mechanical designs, or analyzing rotation in real-world systems, this tool gives you accurate results in seconds.
FAQs
How do you convert rotational energy to kinetic energy?
To convert rotational energy to linear kinetic energy, you look at how the object is moving. If it rolls without slipping, you can calculate both using their respective formulas. It's a little math, but no biggie!
What’s the formula for the rotational kinetic energy of a disk?
For a solid disk, the moment of inertia formula is I = (1/2) m r², so the rotational kinetic energy would be KR = (1/4) m r² ω².
How do you calculate the rotational kinetic energy of a sphere?
A solid sphere’s formula is I = (2/5) m r², so its energy is calculated as KR = (1/5) m r² ω².
What unit is used for rotational kinetic energy?
The standard unit is the Joule (J). You can also use Kilojoules (kJ) or Foot-pounds (ft⋅lb) if needed.
What’s the difference between moment of inertia and rotational mass?
Moment of inertia is like mass for rotation – it tells you how hard it is to change an object’s spin. Rotational mass refers to how the mass is spread out from the axis of rotation.